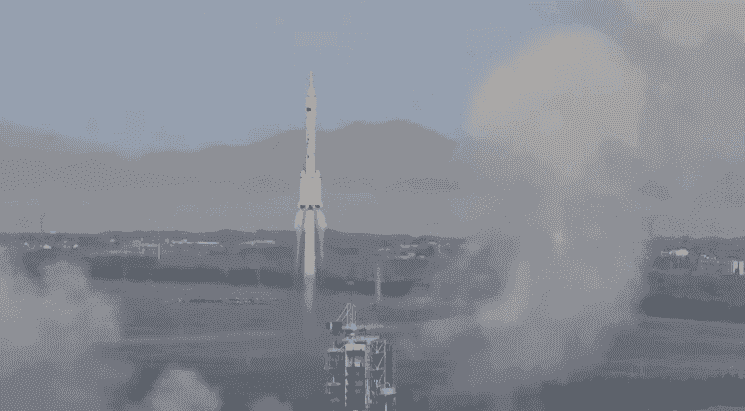
China sent a brand-new crew of three astronauts to the space station on Tuesday in an effort to send people to the moon by the end of the decade.
The crew, which includes China’s inaugural non-military astronaut, will briefly coexist at the Tiangong station with the existing team of three before their return to Earth subsequent to their mission spanning six months.
China’s Ambitious Vision for Its Space Station
The Shenzhou 16 spacecraft was launched from the Jiuquan launch center located near the Gobi Desert in northwestern China. It was carried into space by a Long March 2-F rocket.
Officials of the space program have declared their intentions to expand the station by incorporating an additional module and to initiate a manned mission to the moon prior to the year 2030. China developed its own space station as it was unable to participate in the International Space Station.
This circumstance arose predominantly due to the concerns of the United States regarding the close connection between China’s space program and the People’s Liberation Army, an integral component of the ruling Communist Party.
Read more: The Most Rewarding College Degree In America Leads To Six-Figure Jobs In A Select Field Of 100,000
Advancements in Space Exploration

China became the third country, following the former Soviet Union and the United States, to independently launch a manned space mission in 2003.
During the most recent space mission, Gui Haichao, an expert in payloads from Beijing’s
premier aerospace research institute, will join Maj. Gen. Jing Haipeng is embarking on his fourth space voyage, along with spacecraft engineer Zhu Yangzhu.
They will reside aboard the space station for an approximate duration of five months, during which they will conduct scientific experiments and routine maintenance.
China and the United States are engaged in a competition to achieve milestones in space, which reflects their escalating rivalry for leadership and influence across various domains.
Although the United States currently maintains an advantage in terms of expenditure, supply chains, and capabilities, China has made notable progress in specific areas, such as the retrieval of lunar samples and the exploration of the moon’s far side using a rover.
Despite this rivalry, the two nations have maintained a cordial relationship in their space endeavors.
The United States aims to dispatch astronauts to the moon by the conclusion of 2025, with assistance from private companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin.
This constitutes a renewed endeavor to conduct human space missions. Both the United States and China have successfully deployed rovers on Mars, and China also intends to land a spacecraft on an asteroid, following in the footsteps of the United States.
The space race between China and the United States has been intensifying in recent years, with both nations making substantial investments in their respective space programs.
Read more: Air New Zealand To Require Weighing Passengers Before They Board Planes

