The new team of astronauts will occupy the station for six months and will replace three coworkers who came in June. To test the station’s capacity to accommodate six astronauts, there will be a week-long handover period.
A week-long handover period will be required, in part to test the station’s capabilities to accommodate six astronauts.
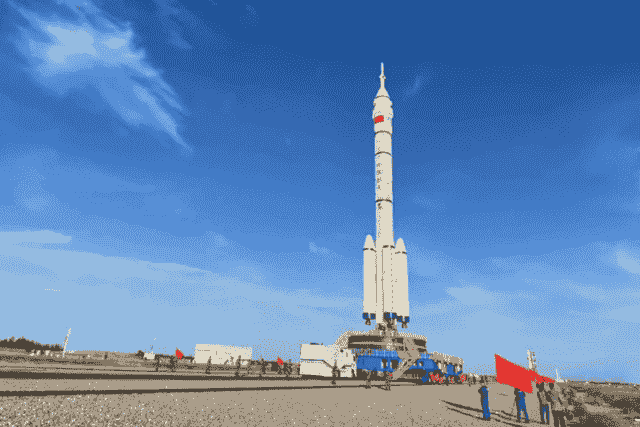
Shenzhou-15 Spacecraft Sends New Chinese Astronauts on Space
The Shenzhou-15 spacecraft, also known as the Divine Vessel, launched on Tuesday from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in the Gobi Desert in northwest China with a new crew aboard.
The station, which will be put together and operate for roughly ten years while conducting experiments in almost no gravity, is currently requiring its final of eleven missions.
The leaving crew is expected to touch down on Earth in the early part of next month.
The installation of facilities and equipment around the space station will be the main emphasis of the next crew, according to a representative for the China Manned Space Administration. By the end of the year, construction is anticipated to be finished.
China’s expanding space capabilities, according to Dr. Christian Feichtinger, executive director of the International Astronautical Federation, are being watched by the globe, he told CCTV, a Chinese official media channel.
The expedition has given Chinese citizens cause for celebration even as the country is still subject to Covid lockdowns and demonstrations. On social media, several people wrote, Long live the motherland.
Fei Junlong, 57, who also served as mission commander on the Shenzhou-6 mission in 2005, is the captain of the Shenzhou-15 crew. He hasn’t done this before.
READ MORE: Medicine for Alzheimer’s: Can Lecanemab Cure the Disease?
Other Countries’ Space Mission

Applicants from Macau and Hong Kong’s special administrative zones, who had previously been barred from the selection process, can now apply to be astronauts for upcoming missions.
The People’s Liberation Army, a branch of the Communist Party in power, is in charge of the program, which has operated mostly independently of foreign assistance. China was denied access to the International Space Station by the US due to the military nature of its space program, even though China has only sometimes worked with other countries’ space programs.
Unmanned mission accomplishments have also been achieved by China; their Yutu 2 rover was the first to explore the little-known far side of the Moon.
For the first time since the 1970s, lunar rocks were also brought back to Earth by China’s Change 5 mission in December 2020, while a different Chinese rover is looking for signs of life on Mars.
While NASA continues with its Artemis lunar exploration program, which aims to send four astronauts on a lunar orbital mission in 2024 and land humans on the moon as early as 2025, officials are reportedly considering a crewed mission to the moon in the future. However, no timeline has been provided.
READ MORE: NASA Halts Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Satellite Due To Skyrocketing Cost; What’s Next?